AI in Chemical Engineering | Automating Scope 3 Compliance
AI in Chemical Engineering: Automating Scope 3 Compliance
Tools and Trends for Engineers Tackling Emissions Tracking Amid Regulatory Crunch
In the high-stakes world of chemical engineering, where global supply chains prioritize speed and scale, Scope 3 greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions-indirect emissions from upstream suppliers, product use, and final disposal-have emerged as the industry’s toughest challenge.
For chemical firms, Scope 3 can represent over 80% of total carbon footprint, far eclipsing emissions released directly in plants or through purchased energy. Yet, only 30% of chemical companies provide credible Scope 3 disclosures (Deloitte, 2025), with voluntary reporting patchy and regulatory pressure mounting.
The Scope 3 Challenge: Why It’s Personal for Process Engineers
Scope 3, as codified by the GHG Protocol’s 15 categories, spans every link in a chemical company’s value chain-from emissions embedded in purchased naphtha and catalysts to downstream incineration of plastics and specialty compounds.
In some segments, downstream product use can account for up to 85% of a refinery’s carbon burden.
Tracking these emissions requires collecting granular, third-party data across continents, often consuming 25% or more of engineering man-hours that could otherwise go toward innovation.
Key 2025 Regulations
| Regulation | Region | Core Requirement | Enforcement / Fine |
|---|---|---|---|
| California SB 253 | USA | Mandatory Scope 3 disclosure for >$1 B firms | Up to $1 M fine; first reports 2027 |
| EU CSRD | EU / EEA | Double materiality; mandatory Scope 3 audits | Up to €10 M penalties |
| EPA Scope 3 Shift | USA | Eliminated EPA support unit → firms fully responsible | Compliance liability shifted to producers |
As a result, process engineers are no longer just operators-they’re emissions accountants, compliance strategists, and digital solution architects.
AI in Action: Turning Regulatory Pain into Engineering Advantage
Artificial intelligence is redefining how chemical engineers handle Scope 3, shifting compliance from a manual burden to a strategic decarbonization opportunity.
1. Real-Time Supply Chain Mapping
Machine-learning (ML) tools now ingest supplier databases, ERP streams, and IoT sensor logs-cross-referencing material flows, emissions factors, and life cycle inventories.
- Upstream emissions for naphtha, ethylene, and rare earths vary by region and transport mode.
- AI models predict emissions spikes caused by port delays or energy market shifts.
- 2025 pilots report 50-70% accuracy improvement over spreadsheets.
2. Generative AI for Scenario Planning
By simulating “what-if” feedstock or route swaps (e.g., bio-naphtha vs fossil feedstock), generative AI models forecast emissions, cost, and yield trade-offs.
90% of large chemical companies now use LLM-based scenario tools, often finding that bio-based feedstock switches can trim Scope 3 by 15-20% with minimal yield loss.
3. Supplier Engagement Automation
AI-powered chatbots and blockchain integrations now engage thousands of suppliers simultaneously, validating data and flagging inconsistencies.
- Covestro + Alibaba Cloud Energy Expert: QR-coded plastic tracking in Asia ensures every kg of recycled polycarbonate is auditable end-to-end.
- Reduces manual supplier surveys by 60% and compliance time by 35%.
4. Multi-Scale Integration
AI now plugs into every layer-from molecular design (graph neural networks for catalysts) to logistics optimization.
75% of chemical producers now trial “multi-silo” Scope 3 AI integration (Omdena 2025).
2025 Benchmark: Scope 3 Emissions in Chemical Production
| Segment | % of Total Emissions (Scope 3) | Common Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Petrochemicals | 80-85 % | Feedstocks, product use, disposal |
| Specialty Chemicals | 68 % | Solvents, complex organics, packaging |
| Fertilizers | 62 % | Mining, processing, field distribution |
| Pharmaceuticals | 59 % | API supply, packaging, healthcare waste |
| Paints/Coatings | 47 % | Pigments, solvents, lifecycle use |
| Industry Average | ≈ 75 % | All up/downstream sources + suppliers |
Table 1 - Typical Scope 3 Share in Major Chemical Segments (Deloitte & Cefic, 2025).
Essential AI Tools for Scope 3 Compliance
| Platform | AI Features | Engineering Application | 2025 Pricing (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pulsora | Hotspot analysis, SBTi/CDP dashboards | Feedstock flows, supply validation | $50K +/yr |
| Sweep | Collaborative dashboards, supplier requests | Vendor data collation | 100K /yr |
| Sphera | LCA + EHS risk modeling | Lifecycle tracking, reg planning | $75K +/yr |
| CO₂ AI | Smart data matching, auto-compliance | Supplier screening, Scope 3 gap filling | $30K +/yr |
| Watershed | Global database + ERP integration | Multi-site firms / cross-border | $100K +/yr |
| Greenly | Proxy auto-fill, rapid deployment | SMEs / growth ops | 50K /yr |
| Microsoft Sustainability Cloud | Copilot engagement, IoT linkage | Real-time plant-to-chain visibility | $5K +/user/yr |
Table 2 - Top AI Platforms for Scope 3 Compliance (Industry Reports 2025).
Case Studies: Innovation at the Frontlines
BASF × Siemens - AI-enhanced digital twins optimizing energy use and forecasting emissions cut Scope 3 by 18% for coatings while raising yields.
Covestro × Alibaba Cloud - Blockchain-linked carbon tracking for recycled plastics cut compliance time by 35%.
Peking University - AI-based industrial park model cut Scope 3 by 25% via material-flow optimization and catalyst reformulation.
Shell - 10,000+ AI sensors and predictive models reduced indirect Scope 3 by 9% in 14 months, saving ≈ $2 M/year.
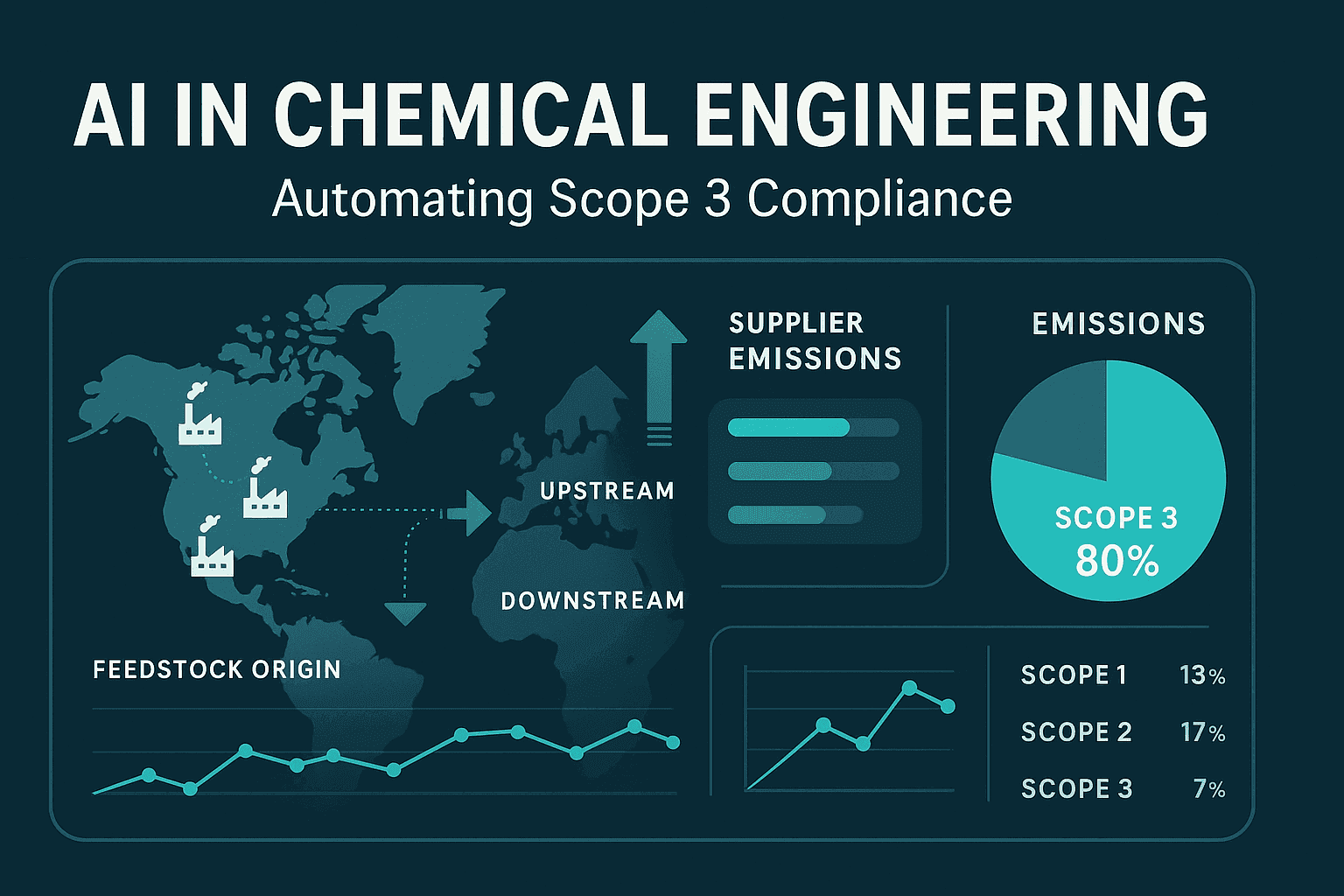
Visual: Scope 3 AI Automation in Chemicals
Suggested Infographic
- Dashboard showing supply-chain mapping: feedstock origins, logistics, process emissions.
- Overlay arrows for upstream/downstream flow.
- Pie chart inset: Scope 1 (7%), Scope 2 (13%), Scope 3 (80%).
(This can be used as a banner or editorial graphic.)
Overcoming Barriers: Data Silos, Bias & Ethics
AI is not a silver bullet-fragmented data and opaque supplier networks persist. Engineers must stay vigilant.
- Bias: Models can embed incorrect emission factors → regulatory risk.
- Security: APIs and blockchains require cyber-hardening.
- Human Factor: Hybrid approach (AI automation + engineer validation) ensures trust.
81% of firms now upskill engineers in digital carbon accounting (EY & WRI 2025).
Regulatory Outlook: Net-Zero by 2030 … or Bust
Chemical producers face tightening mandates under CSRD, SB 253, and TfS Product Carbon Footprint guidelines.
AI adoption is expected to cut Scope 3 emissions by up to 45% by 2030, per WRI scenarios.
Best Practices for Engineers
- Start Now: Use free tools like Persefoni or Greenly for initial audits.
- Integrate: Map supply chains; pilot AI-enabled LCA tools.
- Upskill: Train in AI + GHG Protocol + CSRD/SB 253 frameworks.
- Collaborate: Secure supplier data; use blockchain for verification.
- Document: Maintain audit trails; align to SBTi and CDP standards.
The Road Ahead: AI as Catalyst for Decarbonization and Innovation
For chemical engineers, Scope 3 compliance is no longer a reporting task-it’s a core engineering challenge.
AI transforms compliance into competitive advantage: automating data collection, scenario modelling, and supplier engagement, while unlocking new profit pools through resource efficiency.
Top-tier firms report ROI > 300% in the first year of AI deployment through reduced reporting time and energy savings.
As 2027 reporting deadlines approach, AI-driven Scope 3 management will separate leaders from laggards-defining the next era of cleaner, smarter, and more profitable chemical production.
References
- Deloitte: Emissions in Chemicals Industry
- Addleshaw Goddard: Scope 3 in Chemicals
- CarbonBright: AI for Sustainability
- SmartDev: AI in Chemical Industry Use Cases
- WRI: Chemical Emissions Transparency
- Cefic: Climate Monitoring for Chemicals
- SBTi: Chemicals Sector Guidance 2025
- EPA: Scope 3 Guidance Update 2025
- CO₂ AI Platform & Sustaira: AI Sustainability Platforms
- Illuminem: AI Sustainability Insights (2025)